Maxillary sinus lift for dental implants
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure in which bone material replaces the missing bone and restores the damaged area to place the dental Implant (the minimum height of the bone should be 8 mm). Bone grafting is mainly performed along with the implant in cases of long-term tooth loss. Long and associated with bone loss, or In the case of chronic periodontitis where the bones become thin or eroded.
What is the maxillary sinus lift operation?
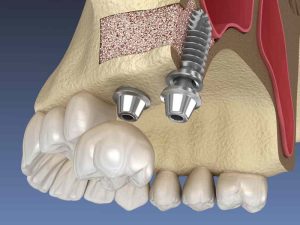
It is a surgical operation aimed at increasing the amount of bone in the posterior maxilla (maxillary bone), in the region of premolars or molars, by lifting the Inferior Schneider’s membrane (sinus membrane) and placing a bone graft.
How is bone grafting and maxillary sinus lift done?
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure in which the missing bone is dissolved with bone material and the damaged area is reconstructed to place dental implants. The desired bone height in the overflow condition should be at least 8 mm.
The procedure is usually done along with the Implant in cases indicated by long-term tooth loss and chronic periodontitis.
Bone grafting is determined after a medical diagnosis that includes x-rays. The surgeon who performs the operation conducts it in different ways using different materials such as artificial, natural or full bone transplantation.
What are the most important technologies used?
Before performing maxillary sinus fundus augmentation, examinations are made to determine the patient’s maxillary sinuses, and panoramic x-rays are taken to depict the patient’s maxillary sinuses and maxillae. In special cases, a CT scan is taken to measure the height and width of the sinus, and to rule out any sinus disease.
There are several variations of the maxillary sinus fundus lift technique:
Traditional sinus fundus augmentation or lateral window technique:
The operation Is performed from the inside of the patient’s mouth, where the surgeon makes an incision In the gums, and once the cut Is made, the surgeon then pulls out the gum tissue, showing the bony side wall of the maxillary sinus, then the surgeon cuts a window Into the sinus, revealing Schneider’s membrane where the membrane is separated The bone graft material is placed In the newly created place, then the gums are sutured closed and the graft Is left for a healing period of 4-12 months.
The graft used can be either an autograft, a contrast graft, an allograft, an organograft (growth factor-infused collagen matrix), or combinations thereof.
Bone cutter technique:
This technique Is performed when the need to raise the bottom of the maxillary sinus Is less than 4 mm, and the osteotomy technique is performed by lifting the posterior gingival tissue and making a cavity In the bone within 1-2 mm of the maxillary sinus membrane, then the floor of the sinus is raised By tapping on the floor of the maxillary sinus using an osteotome, the amount of augmentation that Is achieved using the osteotomy technique Is usually less than what can be achieved using the lateral window technique, and the dental implant is usually placed in the cavity formed at the time of the maxillary sinus lift procedure It is left to overlap with the bone as the bone overlap usually lasts from 4 to 8 months.
The goal of this procedure is to stimulate bone growth and form a thicker sinus floor, in order to support dental implants to replace missing teeth.
Hydraulic compaction of the maxillary sinus:
Unlike traditional methods of maxillary sinus lift, which usually cuts the bone at the lateral side of the upper jaw, the hydraulic sinus compaction technique, or HSC technique, cuts the bone at the lateral side of the maxillary ridge. The HSC technique has shown that the recovery time is shorter than the conventional method. The dental implant is placed at the same time as the maxillary sinus lift, which also reduces the recovery time.
Where the surgeon makes an incision in the gum tissue to reach the bone and begins to cut the bone along the edge and stops the drilling further than the maxillary sinus by about 1 mm, and hydraulic pressure is introduced to the surgical site at this point, providing sufficient force to start the dissection of the membrane non-traumatically in The floor of the maxillary sinus, and once the membrane Is relaxed, the hydraulic pressure stops.
The membrane, when relaxed, is slightly separated from the bone. The bone graft mixture is then packed through the hole and gently pushed against the membrane. This pressure will lift the maxillary sinus slightly, resting it on the newly placed bone.
Once the initial lift is complete, the surgeon drills a cavity Into the bone that will fit Into the new implant and the bone graft material is added again with pressure to increase the lift of the maxillary sinus until the proper height is reached for implant placement, then the surgeon places the dental implant into the bone cavity and sews the gums back In its place.
When do we resort to a maxillary sinus lift?
- Insufficient bone thickness or osteoporosis.
- Erosion of bone tissue with significant loss in the Implant area.
- There is not enough bone tissue to implant the grafts in the area.
- The absence of chronic gingivitis, as this can be achieved by treating gum disease if it is present in the required area.
- A structure with a high level of wound healing capacity and an appropriate level of oral hygiene.
Who are the candidates for the operation?
Patients who have the following may be good candidates for sinus bone augmentation:
- Patients who have lost more than one tooth in the posterior maxilla.
- Loss of a large amount of bone in the posterior upper jaw.
- Missing teeth due to a congenital or genetic defect.
- The patient is without most of the maxillary teeth and needs a strong sinus floor for multiple implants.
What are the advantages of a maxillary sinus lift?
- A routine procedure in the field of oral surgery
- Completely painless process with easy recovery after surgery
- The use of high-quality bone material similar to human bones and completely biologically compatible, non-toxic, and does not harm the body and does not cause any unwanted interaction between tissues
- Complete fusion of the bone graft and the process of osteogenesis using the best bone materials, which guarantee an outstanding level of stability and durability.
What are the complications of a maxillary sinus lift?
Like any surgical procedure, there are potential complications for the patient, which are:
- The pain.
- Infection and inflammation.
- Itching
- Allergic reactions.
- Damage to tissues or nerves.
- Scar formation.
- The occurrence of a hematoma.
- Bait failure.
- Oral antral fistula.
- Bending or loosening of implants.
How long does it take to recover to be able to get a transplant?
It takes between three and six months for the sinus floor augmentation bone to become part of the patient’s normal sinus floor bone, and sometimes it is left in for up to six months before implants are placed. However, some surgeons do bone augmentation and dental implants at the same time to avoid having two surgeries.
The cost of treatment at Zein Hospital
The cost of maxillary sinus lift for dental implants varies according to the patient’s condition, so please contact us and we will provide you with a price quote.
This content has been approved by Zein Clinic doctors
To contact the doctor and provide a free consultation, click here:
Did you like our theme? You can share it with your friends now!
Read more:
The most important tips before and after dental Implants
Sources: NCBI

 واتساب
واتساب